Uniswap has been at the forefront of decentralized finance (DeFi), continually evolving to meet the growing demands of the crypto trading community. With Uniswap V2, launched in May 2020, the platform introduced direct ERC20 to ERC20 swaps, eliminating the need to go through Ethereum (ETH), which optimized trading efficiency and reduced costs. Following that, Uniswap V3 was introduced in May 2021, revolutionizing DeFi with the concept of concentrated liquidity, allowing liquidity providers (LPs) to allocate funds within custom price ranges, thereby maximizing capital efficiency. Now, from July 2023, Uniswap has introduced the development of Uniswap V4 Hooks, which is poised to further transform the DeFi landscape by enabling even greater customization and functionality in decentralized trading protocols.
What is Uniswap V4?
Uniswap V4 announced in early June 13, 2023, is the latest iteration in the Uniswap series, bringing innovative features that aim to enhance user experience and expand functionalities. This version maintains the foundational aspects of automated market-making while introducing ‘hooks.’ Hooks in Uniswap V4 are customizable code pieces that can be attached to liquidity pools, offering Uniswap V4 developers unprecedented control over how pools behave during trades.
The implementation of hooks in Uniswap V4 allows for a modular approach to pool behavior, meaning that specific functions of the trading process can be altered or extended according to the needs of the pool or its creators. For instance, hooks can be designed to execute additional security checks, integrate with external data sources for dynamic pricing, or apply custom logic to modify transaction fees based on real-time trading volume or volatility.
This flexibility opens up a plethora of possibilities for innovation in trading strategies and financial instruments within the DeFi ecosystem. Developers can tailor the liquidity pool’s operations to better serve niche markets or experimental financial models, enhancing the platform’s adaptability and potential for market impact. By enabling more detailed control and customization, Uniswap V4 is set to provide a robust foundation for the future growth and diversification of decentralized finance.
How Uniswap Hooks Work
Uniswap V4 hooks act as entry and exit points in the trading process, allowing developers to embed additional features directly into the pool’s operations. These hooks can be programmed to execute custom logic before or after certain events, such as swaps or liquidity changes, effectively modifying the pool’s standard behavior. This modular approach not only fosters a more dynamic ecosystem but also paves the way for bespoke financial products and services on the Uniswap platform.
In Uniswap V4, these hooks are specifically termed as follows, which clearly define when they are triggered in relation to trading events:
beforeInitializeafterInitializebeforeAddLiquidityafterAddLiquiditybeforeRemoveLiquidityafterRemoveLiquiditybeforeSwapafterSwapbeforeDonateafterDonate
Developers who are proficient in Solidity and understand the Uniswap V4 framework can craft these hooks. Creating a hook involves writing the necessary code in Solidity, conducting thorough tests on Ethereum test networks to ensure its functionality and safety, and then deploying it to the main network. However, due to the significant impact hooks can have on liquidity pool operations, their deployment typically requires a governance approval process within Uniswap’s framework. This process ensures that only secure and beneficial hooks are integrated, maintaining the integrity and efficiency of the pools.
Uniswap V4 architechture
Uniswap V4 introduces a robust architectural enhancement that leverages advanced blockchain technologies to optimize decentralized trading. The key feature of this architecture is the introduction of hooks—specific code snippets that can interact directly with the trading mechanism. These hooks are strategically placed to modify the behavior of liquidity pools during transactions, effectively enabling custom functionalities like dynamic fee adjustments or integrations with external data sources for better market responsiveness.
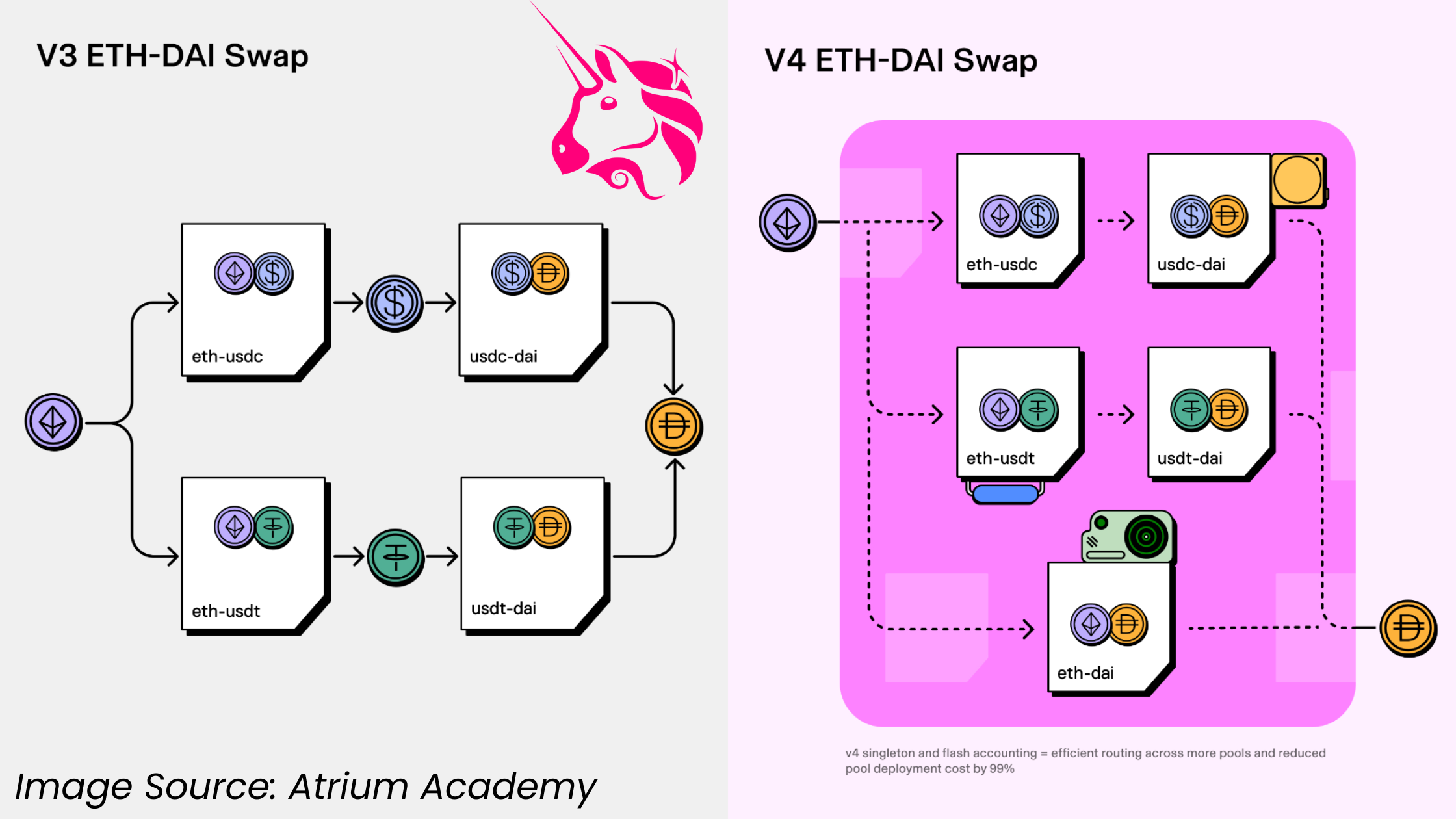
The architecture of Uniswap V4 is designed around a single PoolManager smart contract that manages all liquidity pools. This singleton architecture consolidates all pools into a single contract, significantly reducing gas costs and improving efficiency for pool creation and multi-hop trades. This centralized management system contrasts with earlier versions where each pool was a separate contract, simplifying interactions and enhancing security and performance. This design utilizes Solidity libraries for the pools, allowing the PoolManager to execute all Automated Market Maker (AMM) logic internally without external calls, further reducing transaction costs and increasing efficiency.
Additionally, Uniswap V4 incorporates Flash Accounting, which minimizes gas costs by only moving net balances at the end of transactions, similar to flash loans. This method allows for more complex transactions, such as multi-hop swaps, without the need for multiple token transfers, thus minimizing the gas costs associated with these operations.
Uniswap V4 Release Date
The anticipated release of Uniswap V4 is set for Q3 of 2024. This version is being developed by a team of experienced blockchain engineers and thought leaders in the DeFi space, who have been integral to the success and reliability of previous Uniswap versions. As the release date approaches, the team is focused on ensuring that V4 will be robust, secure, and scalable.
Uniswap Hooks Use Cases
- Dynamic Fee Adjustment: Hooks can be used to adjust transaction fees based on real-time market conditions. For instance, during periods of high volatility, fees could be increased to incentivize liquidity providers, balancing the risks they face from price fluctuations.
- Custom Trading Rules: Developers can implement hooks that enforce specific trading rules within a pool, such as minimum trade sizes or mandatory holding periods, to discourage market manipulation or excessive speculation.
- Integration with External Data: By utilizing hooks, pools can interact with external data feeds or oracles, allowing the implementation of features like price pegs to real-world assets or automated adjustments based on external market conditions.
- Enhanced Security Features: Hooks can enhance security by adding additional checks and balances before transactions are finalized, such as verifying that the transaction does not exceed certain risk parameters.
Developers can leverage Uniswap V4 hooks to create customized DeFi products that cater to niche markets or specific financial strategies. For instance, one could build a derivative platform that uses Uniswap V4 pools, or create tools for automated DeFi portfolio management that adjust a user’s asset allocation based on predefined criteria. Check Awesome Uniswap v4 Hooks repo for hook examples and creative ideas!
How to build a Uniswap Hook
For developers eager to dive into Uniswap V4 hooks, the journey begins with understanding Solidity, the programming language used to write these custom smart contracts. It’s crucial to familiarize yourself with the Uniswap V4 architecture, especially the PoolManager and the lifecycle hooks, which play central roles in how the pools operate.
Setting up your development environment is the next step. Tools like Hardhat or Foundry are essential for deploying and testing smart contracts. Begin by reviewing the Uniswap V4 documentation to grasp the full scope of its architecture and hooks. This foundational knowledge will guide you in writing your first hook. You can start with basic hooks by using templates provided in the v4-template repository, which includes examples and utilities that simplify the development process.
Once you have a basic hook, it’s time to deploy and test it. Deploy your hook on an Ethereum testnet, such as Goerli, to ensure its functionality. Testing rigorously on test networks helps in identifying and fixing issues before deploying on the main network. This step is crucial for maintaining the integrity and security of the pools.
For additional guidance, Uniswap V4 Hooks GPT can be an invaluable resource. This AI tool can help you understand complex concepts, provide code examples, and offer deployment and testing advice. By leveraging these resources, you can efficiently start building and innovating with Uniswap V4 hooks, paving the way for new financial products and strategies in the DeFi space.
For additional guidance, Uniswap V4 Hooks Developer Assistant GPT (requires GPT4) can be an invaluable resource. This AI tool is constantly updated with the latest information and documentation from Uniswap, ensuring that you have access to the most current knowledge as changes occur before the full launch of Uniswap V4. It can help you understand complex concepts, provide code examples, and offer deployment and testing advice. By leveraging these resources, you can efficiently start building and innovating with Uniswap V4 hooks, paving the way for new financial products and strategies in the DeFi space.
Conclusion
Uniswap continues to drive innovation in the DeFi space, with V4 setting a new standard for flexibility and user engagement in decentralized trading. For developers and enthusiasts looking to stay at the cutting edge of blockchain technology, diving into Uniswap V4 now is crucial. A great resource for learning more about Uniswap V4 is atrium.academy, which has received a grant from Uniswap to develop educational programs specifically tailored to this new version. Whether you’re a developer looking to build the next big DeFi application or simply a crypto enthusiast keen on understanding the latest technologies, Uniswap V4 offers a gateway into the future of decentralized finance.